Key Takeaways
- The Global Gig Economy is estimated to have generated $3.8 trillion revenue in 2022 according to a research by the Staffing Industry Analysts estimates.
- A gig worker may be defined as someone who takes up a short-term project or project-based jobs often for multiple clients.
- Gig work definition includes non-standard work consisting of income generating activities outside of traditional, direct-hire employment.
- Ride-hailing, delivery, freelance tech, handymen, content creators, graphic designers, and creative work are some of the gig work categories.
- According to the World Bank, Latin America contributes to nearly $65 million of the global Gig economy.
What is a Gig Worker?
Before we get into “what is a gig worker”, we need to understand “what is a gig work?”. The gig work definition is fairly simple – any non-standard work that is characterized by income generating activities outside of conventional, long-term, direct-hire employment. Now, what is a gig worker? A gig worker is someone who engages in short-term, project based assignments quite often for multiple clients at the same time.
But, what is a freelance gig worker? How important is the gig economy? What is the contribution of gig workers to the global workforce? How to manage gig workers efficiently? This blog explores the gig workforce and economy deeply and introduces an efficient and streamlined way to manage the gig workforce.
What is a Gig Work in today’s economy?
The workforce looks significantly different that it did about a decade ago. What has changed? The gig workforce has become a bigger contributor to the global workforce. The Upwork Research Institute’s 2023 Freelance Forward Survey states that the Gig workforce (freelancers) accounts to a staggering 38% or 64 million of the workforce in 2022. This is a 4 million increase from the past year. Translating this to revenue, American freelancers contributed to approximately $1.27 trillion annual earnings to the U.S economy.
What is gig work and why is it becoming popular? The definition of gig work is a short-term, flexible work arrangement where individuals work independently for one or more clients at the same time rather than being employed in a traditional, long-term goal. Gig work is usually project-based or task-oriented, where workers are often paid on a freelance or contractual basis.
The growing contribution of the gig economy is primarily due to professionals seeking alternatives to traditional 9-5 working models leaning towards more flexible work arrangements. The gig economy is becoming a force to reckon with in the national and global labor market. Gig work involves short-term contracts and freelance work that extends to several work categories.
Some of the popular categories include – asset-sharing services, transportation, skilled professional services, and household tasks. The gig economy has a wider impact on the US and broader global market.
“The gig economy offers enormous opportunities to the staffing industry over the next few years,” said Adam Pode, director of SIA research (EMEA and APAC).
Who is a Gig worker?
Who are gig professionals? A freelancer or a gig worker is someone who takes on short-term or project-based jobs for multiple clients simultaneously. These workers do not have long-term employment contracts, instead earn money by completing individual tasks or projects. Gig work can range from high skilled professionals to on-demand service providers like rideshare drivers and delivery personnel.
What is a freelancer or gig worker?
The terms freelancer or gig worker refer to anyone engaged in temporary, flexible, or freelance work, mostly facilitated through online platforms. Gig workers are also referred to as on-call workers, freelancers, or temporary workers. These workers typically perform work for multiple organizations and clients. To find jobs, gig workers generally use online platforms and work directly with platform’s customers.
Gig workers typically set their own hours and work on projects they choose based on their skills and interests. Gig or freelance workers enjoy a high level of flexibility and an ability to focus on their passions. The work they choose is aligned with their hobbies, interests, aspirations and career goals. Some gig workers consider their work as a pathway to financial stability, while others may consider it as a source of additional income.
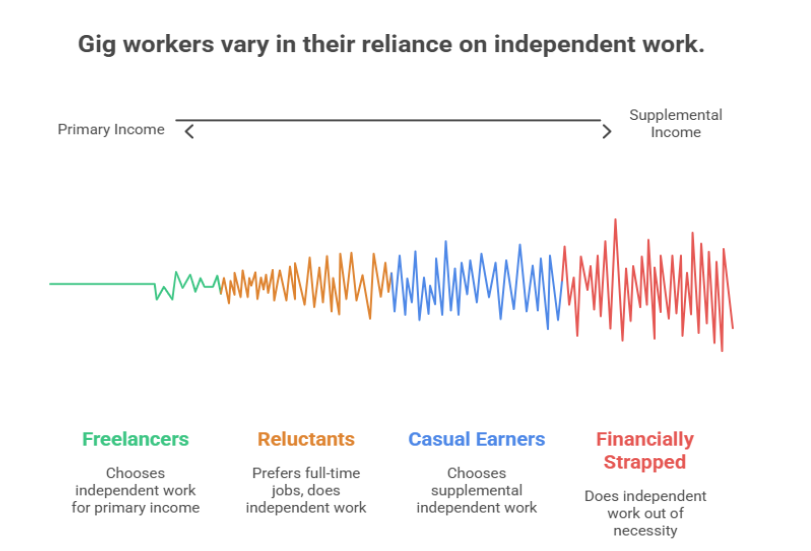
Now that we are clear on “what is a gig economy worker”, let us look into the different types of gig workers. With the gig economy flourishing, many opportunities tailored to diverse skill sets are cropping up across industries. Popular categories of gig workers according to McKinsey include:
- Freelancers – These gig workers choose independent work and get primary income from it.
- Casual earners – These gig workers choose to do supplemental independent work.
- Reluctants – These gig workers do independent work but prefer full time jobs.
- Financially strapped – These workers do supplemental independent work out of necessity.
The Gig economy has risen in popularity through platform apps, and gig work has expanded to many different industries driven by its flexibility and scalability. Also, certain job types naturally lend themselves to gig work because they require short-term commitments and can be performed remotely. The gig workers community continues to grow as more individuals and businesses are seeing the benefits of this model. Common types of gig jobs include –
Rideshare drivers – Platforms like Uber and Lyft provide on-demand transportation. These workers work on contract basis and are paid based on their ride volumes.
Delivery couriers – Apps such as DoorDash and Instacart connect gig workers with food, grocery, and package delivery tasks.
Content creators – Content writers often take short-term contracts for producing blog posts and other copywriting tasks for companies. Freelance writing offers flexibility to write for various clients on diverse topics.
Graphic designers – Businesses are always on the lookout for logos, infographics, and more. Professionals who are proficient in design software and have creative skills can work as graphic designers. Gig workers in design handle projects ranging from logos to end-to-end branding, offering creative solutions to businesses.
Handyman – Services like TaskRabbit assign complete physical tasks like furniture assembly, plumbing, repairs, and moving assistance to workers.
Online tutoring – The education sector has witnessed a shift towards e-learning. To work as a tutor you need subject matter expertise, teaching skills, and patience. All classes are taken virtually.
Gig Workers’ Role in the Workforce
According to the Staffing Industry Analysts (SIA), the revenue generated by the gig workforce totaled $3.8 trillion in 2022. The research reflected data from 18 countries and gig work conducted on a B2B basis. The gig work definition according to SIA includes –
- Temporary workers assigned through a staffing agency
- Temporary workers source directly (not through a staffing agency)
- Self-employed with no employees (independent contractors)
- Statement of work (SoW) consultants employed by consulting firms
- Temporary workers obtained via talent and work services platforms
Growth of the gig economy has a significant impact on both the U.S. and broader global economy. The Freelance Forward 2023 report shows that freelancers contributed $1.27 trillion to the U.S. economy earnings in 2023. Just how big is the gig economy? There are multiple ways to estimate the size of the gig economy.
Some counts include anyone who has ever done any form of non-standard work; while others look at only particular types of work. One of these studies or estimates reveal that more than a quarter of workers participate in the gig economy in some capacity. One of the ways to measure gig workers is to consider anyone who engages in non-standard work in any form with regular or occasional participation, and either for primary or supplemental earnings. According to such counts, by 2025 42 million people in the United States are engaged in some form of gig work.
According to Contingent Worker Supplement (CWS) administered by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 10.2% of workers rely on alternative arrangements for their main job, which includes temp agency work, on-call work, and freelancing.
How do gig workers contribute to the workforce? Gig workers make significant contributions to the workforce by offering a flexible and diverse talent pool, especially in industries like ride-hailing, freelancing, and food delivery. Key aspects of Gig worker contributions include –
Increased workforce participation– Gig work provides opportunities to individuals to participate in the workforce, who otherwise may be excluded from the workforce.
Economic growth – What is a gig economy worker’s contribution to the GDP? The gig economy’s contribution to GDP is expected to grow, with estimates suggesting it could reach 2.5% in some regions.
Flexibility and adaptability – Gig workers offer businesses a flexible workforce that can be scaled up or down based on demand.
Micro-entrepreneurship – The gig economy fosters a spirit of micro-entrepreneurship as individuals can leverage their skills and talents to create their own income streams.
Addressing gaps in workforce – Gig work helps address market needs by providing access to specialized skills and talent on demand, which allows businesses to fill specific roles without the commitment of full-time employment.
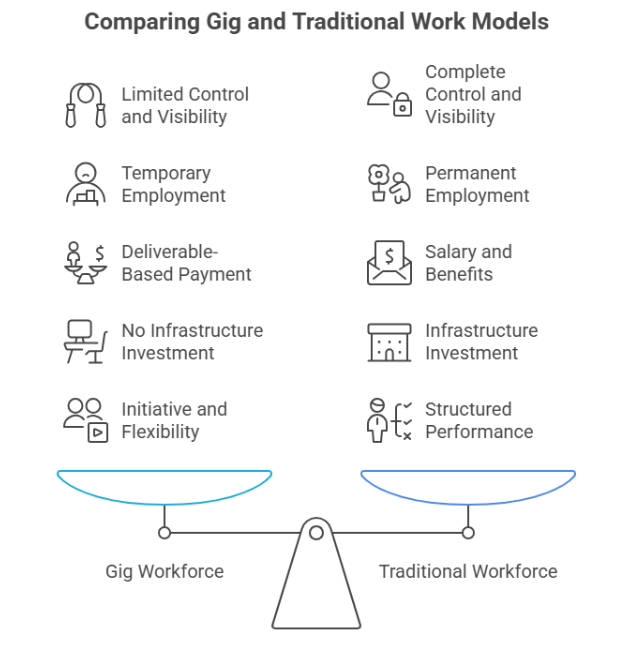
Gig Workforce versus Traditional Workforce
The gig workforce differs from the traditional workforce in several aspects. Understanding these differences helps employers streamline the gig workforce management process.
Managing the Gig Workforce
Going by the trends in the gig workforce, the global workforce will have multiple jobs in future. With the labor market progressively characterized by short-term contracts, flexible gig workforce, and freelance work, it becomes challenging to manage the gig workforce with archaic methods. Here are some best practices to follow for effective management of the gig workforce
1. Prioritize communication
Since gig workers are not full-time salaried employees, managers that enlist their services must understand that they will not have spontaneous face time with these workers and cannot call immediate meetings for addressing issues. It is important to be flexible with the format of meetings and maintain seamless communication. Employers must also be flexible with their method of communication, understanding that gig workers have several clients filling their working hours.
2. Set realistic productivity expectations
Gig workers are their own bosses, typically filling their workdays with projects on a first come, first serve basis. The pressures faced by gig workers are different from that faced by traditional full-time employees. Gig workers need to deliver quality work on time or they may risk being replaced. Employers need to understand that productivity of gig workers should not be taken for granted. When you find a gig worker producing quality work at a fast pace, you should celebrate their contributions instead of unloading an unrealistic workload on them.
3. Hire the best talent
Employers need to hire talent based on the skills they showcase. The gig workforce offers a wide variety of talent suitable for various industries. Employers need to hire the best talent that aligns with the skill requirements.
4. Effective contract management
Draft a contract that lists clear expectations on compensation and benefits. Since employers cannot have in person conversations or meetings with gig workers, the contract acts as the only way to communicate details with the gig worker.
5. Team management tools
It is a good idea to integrate gig workers with traditional employees through team management tools. This way gig employees feel that they are an important part of the workforce. You also need to put in place effective performance and communication tools to maintain sufficient performance.
6. Performance expectations and management
The management, discipline, and performance review process for gig workers is different from that of regular employees. The lack of in-person meetings with gig workers makes it difficult to manage them like regular workers. Even disciplinary action against performance issues with gig workers also should not be taken like they would do against regular employees.
Regardless of the type of gig worker needed, employers need to understand that their gig workforce operates differently than their traditional, in-office workers. Managers may need to adapt to a new communication style and adjust expectations regarding availability. Employers need to ensure that the gig workers feel they are part of your team.
Are Gig Workers Employees or Independent Contractors?
Clarity on whether gig workers are employees or independent contractors is entirely on the employer. The employer needs to decide on the way gig workers need to be positioned. For example, when a marketing agency maintains a steady gig workforce of content writers who are assigned to various projects can be considered as employment. However, gig workers are predominantly classified as independent contractors due to the degree of control they have over their work schedule and timings.
The IRS considers gig workers as independent contractors, some states however make a distinction between the two. Aside from the legal implications, there are other key differences between gig workers and independent contractors. Gig workers typically use online platforms to find work and carry out their work.
They also have a business structure that covers limited liability corporations and limited control over work’s contractual terms, compared to independent contractors. Independent contractors on the other hand are professionals with a skill set or trade experience gained by working with other businesses.
How Quflo Simplifies Gig Workforce Management
Unlike the traditional workforce, the gig workforce requires a management system that caters to their style of working. Quflo is a gig workforce management solution that caters to specific requirements in managing the gig workforce. With Quflo, you can track work progress, assign gig workers to jobs, maintain time and attendance log, and perform many more functions that can streamline gig workforce management.
Quflo is designed to empower project managers and business owners to manage their gig workforce, contractors, freelance, and part-time workers efficiently. You can manage work schedules and allocations, track worker time, and boost productivity and optimize resource utilization with this all in one gig workforce management solution. This is a mobile-first workforce management app that enables you to manage your gig workforce from anywhere, at any time.
Key Features of Quflo –
Complete workforce management
You can manage your gig workforce effectively with Quflo. The intuitive dashboard provides a complete overview of workers status and task allocations. Complete information on total workers, number of workers on leave, and work status is provided by the dashboard. You even get leave notifications on the dashboard.
Workers management
Quflo has been designed keeping in mind the unique requirements that come with managing a gig workforce. You can track your workers, assign them into groups, track their time, and also get real-time reports on each worker through Quflo.
Time tracking
A detailed view of the time of gig workers can be obtained from Quflo. The time tracking feature allows you to view the workers in each shift, workers in leave, and get their time log details.
Quflo lets you be on top of your gig workforce by streamlining and simplifying the process. This mobile-first app gives you complete control over your gig workforce and makes time, attendance, and gig worker management effortless.
Conclusion
The gig economy has risen steadily over the past few decades, redefining the way work gets done. Through this blog we have covered the basics of gig work – starting from what is a gig work to what is a gig worker to what is a freelancer. While individuals choose to embrace gig work for a variety of reasons, employers or business owners are constantly looking for ways to manage their gig workforce.
Quflo is a complete gig workforce management solution that is easy to use. If you would like to explore our mobile-first gig workforce management solution, contact us at support@quflo.app today.
FAQs
Is freelance work considered as gig work?
Yes, freelance work can be considered as gig work.
Are independent contractors the same as gig workers?
While independent contractors can be considered as gig workers, there is a difference between the two in terms of skill set and contractual obligations.
Can AI replace gig workers?
While AI may automate some tasks in the gig workforce, human-centric creative work cannot be replaced by AI.

